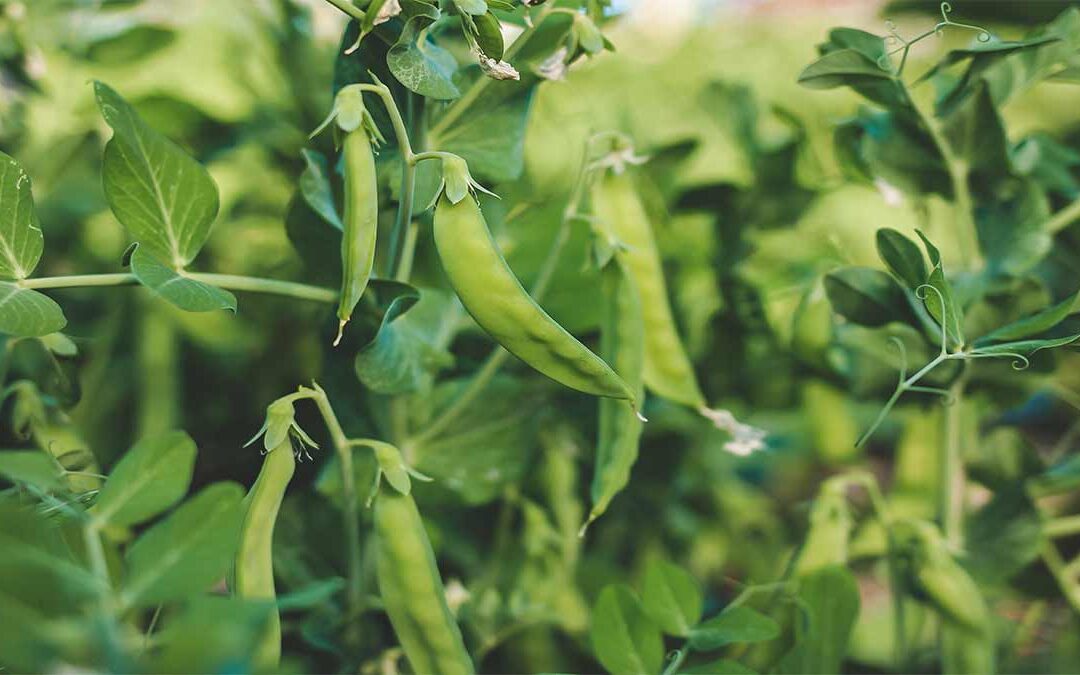
Companion plants for peas can transform your garden into a thriving, pest-free oasis. By thoughtfully selecting the right plant companions, you boost the growth and health of your peas and enhance the entire vegetable garden’s productivity. Companion planting with peas involves strategically placing plants that benefit each other, creating a symbiotic environment that enriches the soil, deters pests, and maximizes garden space.
Good Companion Plants for Peas
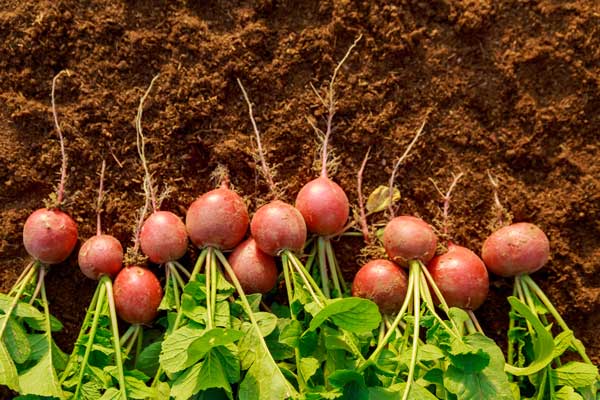
Radish
Radishes are excellent companion plants for peas, creating a harmonious relationship in your garden. When you plant radishes alongside peas, they help loosen and aerate the soil, which benefits the growth of pea roots. Radishes mature quickly and can be harvested early, allowing your peas to spread out.
Radishes can deter pests like cucumber beetles and squash bugs, protecting your pea plants from damage. They are low-maintenance and grow well in cooler temperatures, which aligns with the growing season of peas. However, ensure that radishes stay within your peas by harvesting them in time.
Read More: Radish Companion Plants

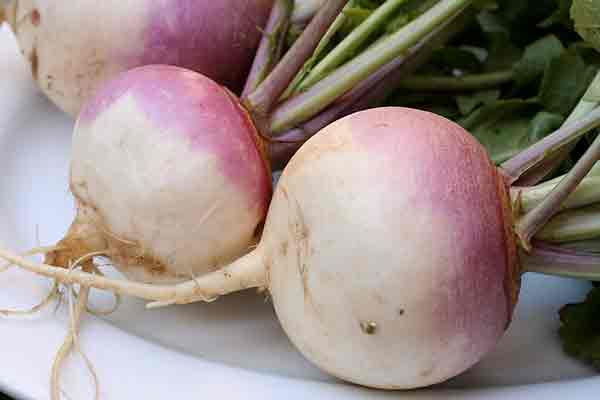
Turnip
Turnips are another fantastic companion plant for peas. Their deep roots help break up the soil, improving drainage and nutrient availability for the peas. This relationship enhances the overall health of your garden soil.
Turnips can help repel pests like aphids and flea beetles, which can harm pea plants. They also provide shade to the soil, keeping it cool and moist, which peas love. Be mindful of their space, and thin turnip plants if necessary to avoid overcrowding your peas.
Read More: Turnip Companion Plants

Lettuce
Lettuce pairs wonderfully with peas, creating a mutually beneficial garden duo. Lettuce’s shallow roots do not compete with the deeper-rooted peas, allowing both plants to thrive without hindrance.
Lettuce provides excellent ground cover, reducing weed growth and retaining soil moisture for your peas. It also benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, resulting in lush, green lettuce leaves. Ensure your lettuce receives enough sunlight by occasionally thinning dense pea foliage to maintain balance.
Read More: Lettuce Companion Plants

Carrot
Carrots and peas make a dynamic gardening pair. The relationship between these two plants is particularly beneficial because carrots help loosen the soil around pea roots, facilitating better growth.
Carrots can enhance soil health by breaking up compacted areas, allowing peas to access nutrients more efficiently. Both plants attract beneficial insects, promoting a healthy garden ecosystem. However, keep an eye on soil depth, as carrots need space to grow downward, while peas prefer to spread out.
Read About: Carrot Companion Plants

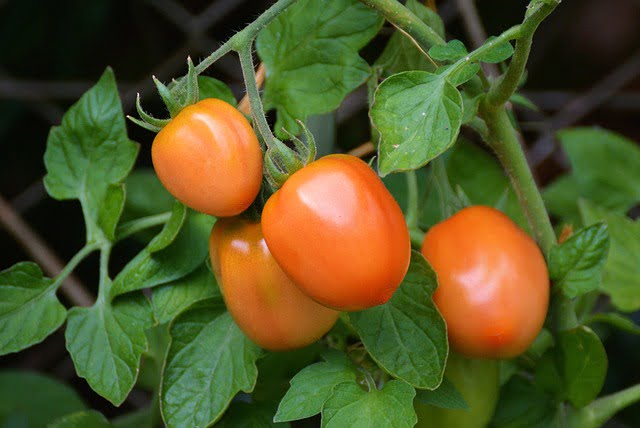
Tomato
Tomatoes and peas seem unlikely, but they complement each other well in a garden. Peas provide natural support for climbing tomato vines, creating a vertical gardening success story.
Tomatoes benefit from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, leading to healthier and more productive tomato growth. Additionally, the shade provided by tomato plants helps protect peas from excessive heat. Ensure you provide adequate support structures to manage the growth of both plants, as they can become quite vigorous.
Read About: Tomato Companion Plants

Cucumber
Cucumbers are excellent companion plants for peas, creating a beneficial relationship in your garden. The sprawling nature of cucumbers complements the vertical growth of peas, maximizing garden space efficiently.
Cucumbers love the nitrogen that peas fix in the soil, resulting in healthier, more productive cucumber plants. Peas can provide a natural trellis for climbing cucumbers, improving air circulation and reducing disease risk. However, ensure cucumbers do not overshadow the peas by guiding their growth along trellises.
Read About: Cucumber Companion Plants

Kohlrabi
Kohlrabi is a fantastic companion plant for peas, contributing to a healthy and productive garden. This cool-weather crop perfectly complements peas regarding growth habits and soil preferences.
Kohlrabi benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, leading to robust bulb development. Its leaves can provide light shade to the soil, helping to retain moisture for the peas. However, ensure proper spacing to prevent overcrowding and resource competition, allowing both plants to thrive.
Read About: Kohlrabi Companion Plants
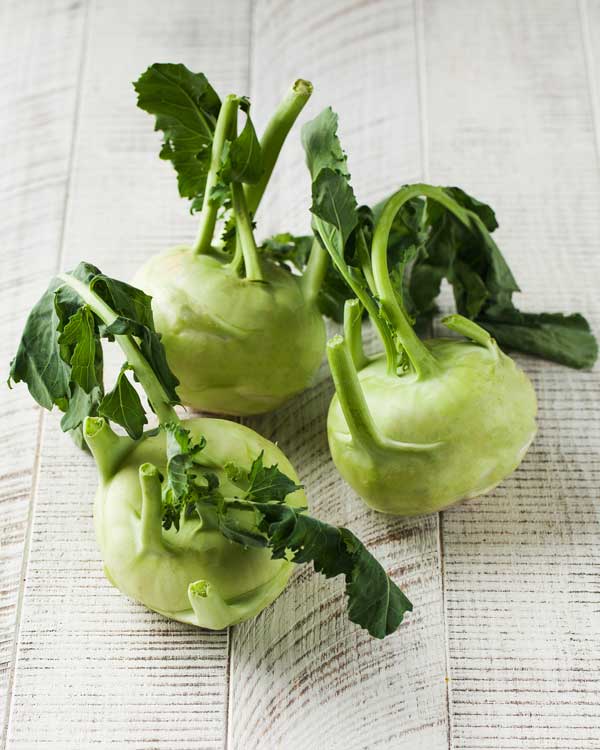

Zinnia
Zinnias are beautiful and beneficial companion plants for peas. These vibrant flowers add color to your garden while providing essential ecological benefits.
Zinnias attract pollinators and beneficial insects like ladybugs and parasitic wasps, which help control pests that can harm pea plants. They also provide a visual appeal, making your garden more attractive. Plant zinnias around the edges of your pea garden to avoid overshadowing the peas, ensuring both plants receive adequate sunlight.
Read About: Zinnia Companion Plants
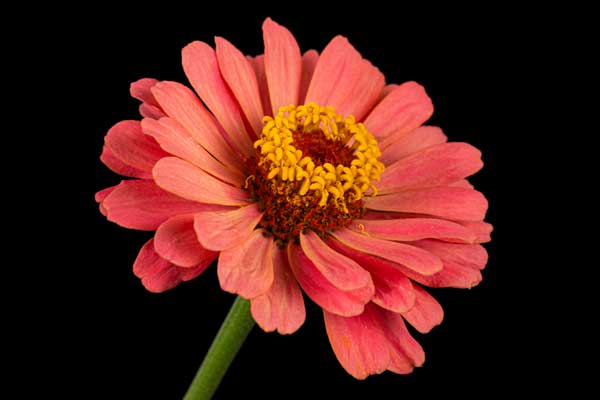

Arugula
Arugula pairs well with peas, creating a harmonious and productive garden environment. Both plants enjoy cooler temperatures, making them ideal companions for spring and fall gardens.
Arugula benefits from the nitrogen-enriched soil provided by pea plants, resulting in tender, flavorful leaves. It also grows quickly, allowing for multiple harvests throughout the season. To maintain a balanced garden, ensure arugula is harvested regularly to prevent it from overshadowing the peas.
Read About: Arugula Companion Plants
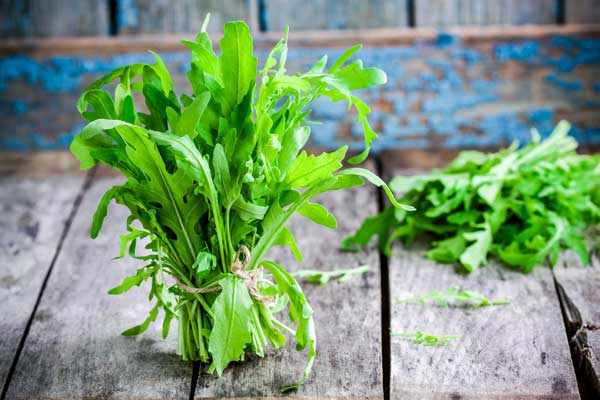

Bok Choy
Bok choy is an excellent companion plant for peas, thriving in similar growing conditions. This leafy green enhances the overall health of your garden.
Bok choy benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, promoting lush, healthy growth. It also provides ground cover, reducing weed competition and retaining soil moisture for peas. Ensure bok choy is spaced adequately to avoid overcrowding and competition for light and nutrients.
Read About: Bok Choy Companion Plants

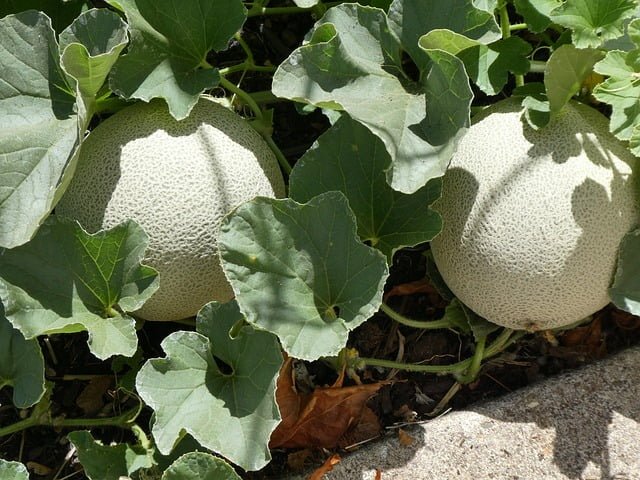
Cantaloupe
Cantaloupe is a surprising but effective companion plant for peas. The sprawling vines of cantaloupe can coexist well with the vertical growth of peas, making efficient use of garden space.
Cantaloupe benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, leading to sweeter, more productive melons. Peas can provide a natural trellis for cantaloupe vines, improving air circulation and reducing disease risk. However, ensure that cantaloupe vines stay within the peas by guiding their growth along trellises or supports.
Read About: Cantaloupe Companion Plants

Asparagus
Asparagus is a perennial companion plant for peas, offering long-term benefits to your garden. Both plants thrive in well-drained soil and cooler temperatures, making them suitable partners.
Asparagus benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, resulting in stronger, healthier shoots. Peas can help deter asparagus beetles, reducing pest pressure on asparagus. Ensure that asparagus has established itself before planting peas nearby to avoid competition during its early growth stages.
Read About: Asparagus Companion Plants

Artichokes
Artichokes are excellent companion plants for peas, creating a mutually beneficial relationship in your garden. Their large, sturdy plants complement the growth habits of peas.
Artichokes benefit from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, promoting robust growth and development. Peas can climb the sturdy stems of artichokes, providing natural support and saving garden space. Ensure proper spacing to avoid competition for nutrients and light, allowing both plants to flourish.
Read About: Artichokes Companion Plants

Sunflower
Sunflowers are excellent companion plants for peas, bringing beauty and practical benefits to your garden. These tall, vibrant flowers create a striking contrast with pea plants.
Sunflowers attract pollinators and beneficial insects, improving the overall health of your garden. They can provide natural support for climbing peas, reducing the need for trellises. However, ensure sunflowers are planted on the north side of your garden to avoid casting too much shade on your peas.
Read About: Sunflower Companion Plants

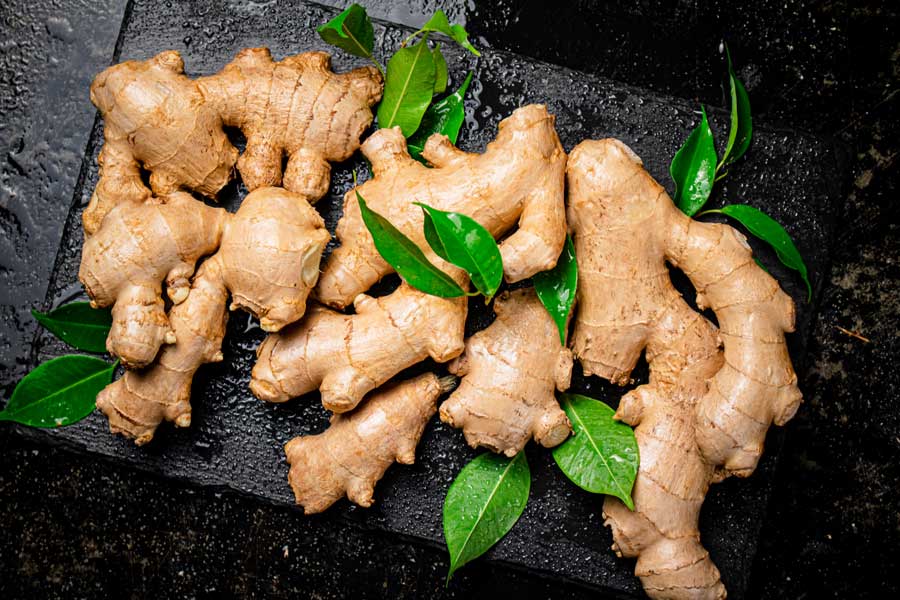
Ginger
Ginger is an intriguing companion plant for peas, offering unique benefits to your garden. Both plants can thrive in similar soil conditions, creating a harmonious growing environment.
Ginger benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, resulting in healthier, more productive rhizomes. It also helps deter pests like aphids and spider mites, which can damage pea plants. Ensure ginger is planted in well-drained soil and receives adequate moisture to support the growth of both plants.
Read About: Ginger Companion Plants

Beet
Beets and peas are a great match in the garden. Beets grow well in the cooler temperatures that peas prefer, and their root structures do not compete, allowing both plants to flourish.
Beets benefit from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, leading to robust root development. They also help break up and aerate the soil, which benefits pea root health. To maintain a balanced garden, ensure beets have enough space to grow without crowding the peas.
Read About: Beet Companion Plants

Marigold
Marigolds are superb companion plants for peas, offering a host of benefits that enhance the health and productivity of your garden. Their bright flowers add beauty while providing significant pest control.
Marigolds repel various pests, including aphids and nematodes, which can harm pea plants. They also attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and parasitic wasps. Plant marigolds around the perimeter of your pea garden to create a natural pest barrier. Ensure they do not overshadow the peas by planting them at the edges.
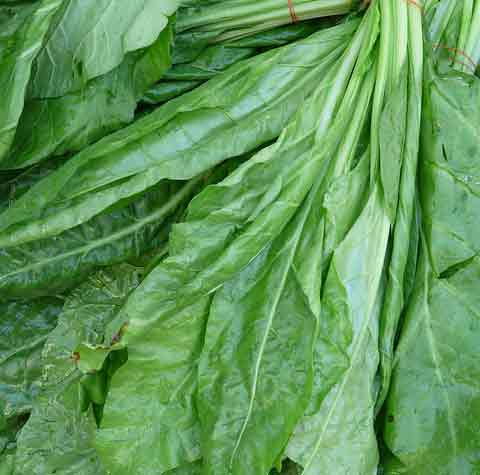
Spinach
Spinach pairs wonderfully with peas, creating a mutually beneficial relationship. Both plants enjoy the cooler temperatures of early spring and fall, making them ideal garden companions.
Spinach benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, resulting in lush green leaves. It also provides excellent ground cover, reducing weed growth and retaining soil moisture for peas. To maintain a balanced garden, ensure spinach receives enough sunlight by thinning out dense pea foliage if necessary.
Read About: Spinach Companion Plants

Dill
Dill is an excellent companion plant for peas, bringing several benefits to your garden. Its feathery foliage does not compete with peas for sunlight or nutrients, allowing both plants to thrive.
Dill attracts beneficial insects like ladybugs and parasitic wasps, which help control pests that can damage pea plants. It also improves the flavor and growth of peas. However, avoid planting dill near carrots, which can stunt their growth—plant dill in a location where it can benefit the peas without interfering with other sensitive plants.

Cilantro
Cilantro is a fantastic companion plant for peas, enhancing your garden’s overall health and productivity. Its aromatic leaves and flowers attract beneficial insects and improve the growth environment for peas.
Cilantro helps repel harmful pests like aphids and spider mites, which can damage pea plants. It also attracts beneficial insects such as hoverflies and lacewings. To maintain harmony in your garden, ensure cilantro has enough space to grow without overcrowding the peas, and consider succession planting for a continuous supply.

Lemon Balm
Lemon balm is a fantastic companion plant for peas, offering numerous benefits to your garden. Its aromatic leaves not only enhance the garden’s scent but also attract beneficial insects.
Lemon balm attracts pollinators and beneficial insects like bees and hoverflies, which can improve the overall health of your garden. Its strong scent helps repel pests like mosquitoes and aphids that might otherwise damage pea plants. Plant lemon balm near your peas, but ensure it has enough space to grow without overshadowing the peas. Regular pruning can help maintain its shape and prevent it from becoming invasive
Read About: Lemon Balm Companion Plants
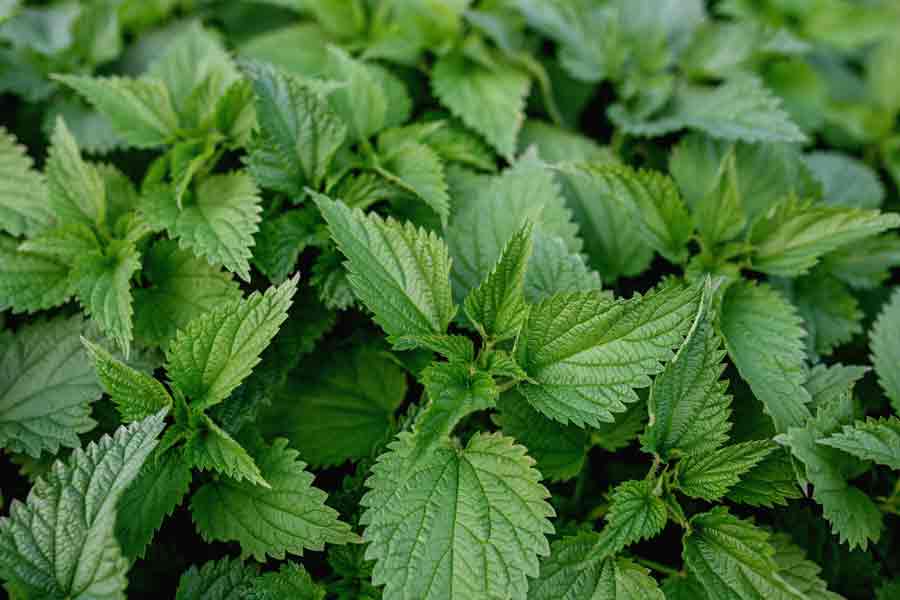

Chive
Chives make excellent companion plants for peas, contributing to a healthy garden ecosystem. Their aromatic leaves help deter pests and attract beneficial insects.
Chives repel pests like aphids and spider mites, which can harm pea plants. They also attract pollinators that help improve garden productivity. Plant chives around the base of your peas, ensuring they do not overshadow the pea plants and receive enough sunlight.
Read About: Chive Companion Plants
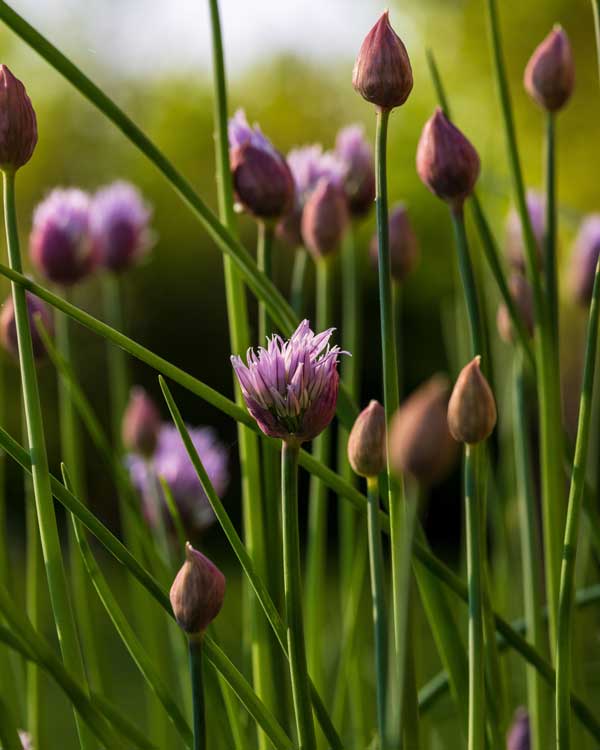

Sweet Potato
Sweet potatoes are fantastic companion plants for peas, creating a beneficial ground cover. Their sprawling vines complement the vertical growth of peas, optimizing garden space.
Sweet potatoes benefit from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, resulting in healthier tubers. The vines provide excellent ground cover, reducing weed growth and retaining soil moisture. Ensure sweet potato vines do not overshadow the peas by guiding their growth along the ground.
Read About: Sweet Potato Companion Plants
Borage
Borage is an excellent companion plant for peas, bringing both beauty and functionality to your garden. Its star-shaped blue flowers attract beneficial insects and enhance the garden’s aesthetics.
Borage attracts pollinators such as bees, which can help improve the pollination and productivity of your garden. It also helps deter pests like tomato hornworms and cabbage worms, providing a natural pest control system. Additionally, borage improves soil health by adding trace minerals and composting well. Plant borage near your peas to take advantage of its benefits, ensuring that it does not overshadow the peas by maintaining proper spacing and pruning if necessary
Read About: Borage Companion Plants

Zucchini
Zucchini can be a great companion plant for peas, especially when space is managed effectively. Their sprawling nature complements the vertical growth of peas, maximizing garden efficiency.
Zucchini benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, leading to healthier and more productive vines. Peas can climb on zucchini stems, saving space and improving air circulation. Ensure zucchini does not overshadow peas by guiding its growth and providing adequate support.
Read About: Zucchini Companion Plants

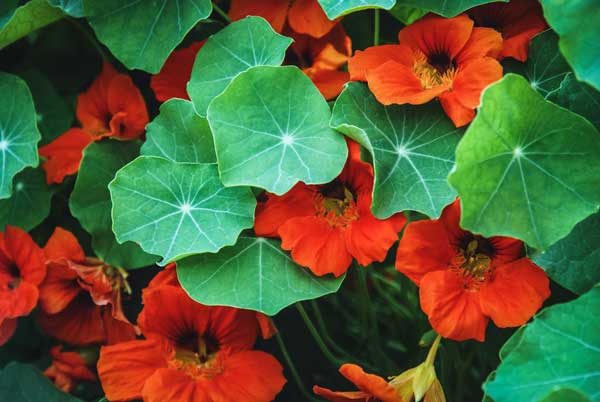
Nasturtium
Nasturtiums are superb companion plants for peas, adding beauty and functionality to your garden. These vibrant flowers attract beneficial insects and repel pests, creating a healthier environment for your peas.
Nasturtiums attract pollinators and beneficial insects like ladybugs and parasitic wasps, which help control pests that can harm pea plants. They also repel aphids and other harmful insects. Plant nasturtiums around your pea garden to create a natural pest barrier while enhancing the garden’s visual appeal.
Read About: Nasturtium Companion Plants

Sorrel
Sorrel is a fantastic companion plant for peas, contributing to a thriving and diverse garden. Its tangy leaves flavor your dishes and benefit the overall garden ecosystem.
Sorrel benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, resulting in lush, healthy growth. It provides excellent ground cover, reducing weed competition and retaining soil moisture for peas. Ensure sorrel has enough space to grow without crowding the peas, and consider harvesting regularly to prevent overshadowing.
Read About: Sorrel Companion Plants
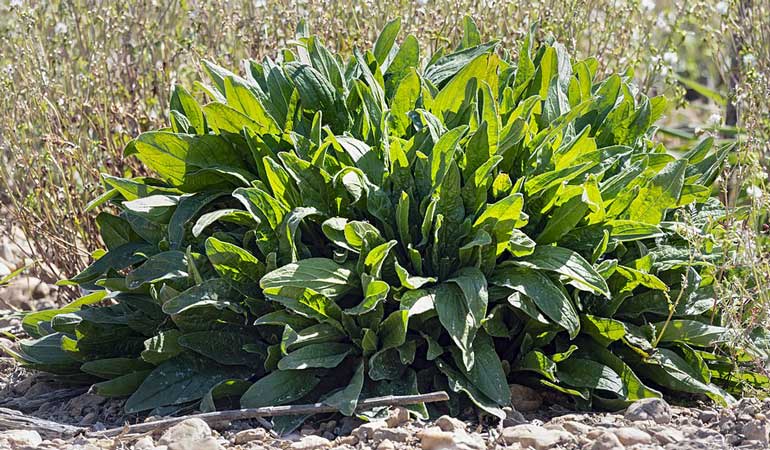

Celery
Celery makes an excellent companion plant for peas, enhancing garden productivity and health. Both plants thrive in similar soil conditions, creating a harmonious growing environment.
Celery benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, leading to stronger, more vigorous growth. It also helps repel pests like aphids and whiteflies. Ensure proper spacing to avoid competition for nutrients and light, allowing both plants to flourish.
Read About: Celery Companion Plants

Pumpkin
Pumpkins are surprising yet effective companion plants for peas. Their sprawling vines can coexist well with the vertical growth of peas, making efficient use of garden space.
Pumpkins benefit from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, leading to healthier and more productive vines. Peas can provide a natural trellis for pumpkin vines, improving air circulation and reducing disease risk. Ensure pumpkin vines stay within the peas by guiding their growth along trellises or supports.
Read About: Pumpkin Companion Plants

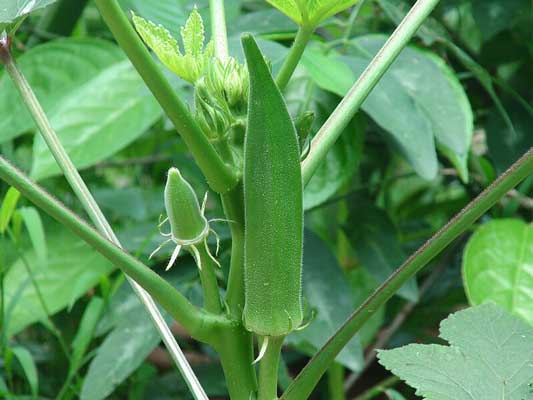
Okra
Okra is a fantastic companion plant for peas, offering unique benefits to your garden. Both plants can thrive in similar soil conditions, creating a harmonious growing environment.
Okra benefits from the nitrogen fixed by pea plants, resulting in healthier, more productive pods. It also helps deter pests like aphids and spider mites, which can damage pea plants. Ensure okra is planted in well-drained soil and receives adequate moisture to support the growth of both plants.
Read About: Okra Companion Plants

By incorporating these companion plants for peas, you create a thriving, balanced, and productive garden. Each plant brings unique benefits, enhancing the growth and health of your peas while contributing to a diverse and beautiful garden ecosystem.
FAQ: Pea Companion Plants
What are good companions for peas?
Companion plants for peas include radishes, turnips, lettuce, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers, beets, broccoli, and marigolds. Each plant brings unique benefits to the garden when grown with peas. These plants make good companions for peas because they provide complementary nutrients or help with pest management. For instance, peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which nearby plants like cucumbers and tomatoes love. Meanwhile, aromatic herbs and marigolds keep pests away with their strong scent. Proper spacing and understanding of each plant’s sun and water needs will ensure your entire garden thrives.
Why should I avoid planting peas near the allium family?
Onions, garlic, and other allium family members do not grow well near peas. These plants release compounds that can stunt pea growth and inhibit their ability to fix nitrogen in the soil. Planting them next to each other may result in nutritional competition and poor overall development of both plants. Planting alliums far from your pea crops is best to keep your garden healthy.
How do peas benefit their companion plants?
Peas grow and provide nitrogen to the soil, benefiting their companion plants. As peas grow, they fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching the soil around the base of the peas. This natural process reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. It promotes the healthy growth of nearby plants, such as early potatoes and many vegetables that love nitrogen. Additionally, planting peas with suitable companions can enhance the entire garden’s productivity.
What are some plants to avoid planting near peas?
Avoid planting peas near onions, garlic, and other allium family members. These plants can interfere with peas’ growth by releasing substances that inhibit their nitrogen-fixing ability. Additionally, brassicas like cabbage can also compete for the same nutrients, making them poor companions. Keeping these plants separate from peas will ensure better growth and yield.
Can I plant aromatic herbs with peas?
Aromatic herbs can be great companions for peas. Herbs such as mint and marigolds have a strong scent that repels common pea pests, creating a natural pest management system. This reduces the need for chemical pest control, allowing peas to grow more robustly. However, ensure that vigorous growers like mint refrain from crowding out the peas by planting them in containers or a separate garden section.
How do cucumbers benefit from being planted near peas?
Cucumbers grow well with peas due to their nitrogen needs. Peas provide nitrogen to the soil, which cucumbers love, promoting healthier and more productive cucumber plants. Additionally, both plants enjoy similar growing conditions and can share garden space efficiently. Ensure consistent watering to meet both plants’ needs.
Are tomatoes good companions for peas?
Tomatoes can be beneficial companions when planted with peas. Peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which helps tomatoes grow strong and healthy. In return, tomatoes can provide a structure for pole beans and peas to climb efficiently using vertical garden space. However, be cautious about watering, as tomatoes prefer slightly drier conditions than peas.
When is the best time to plant peas?
Peas grow well when planted in early spring or late summer. They thrive in cool weather, so it’s best to start them as soon as the soil can be worked in the spring or later in the summer for a fall harvest.
What plants make good garden mates for peas?
Peas have several great garden mates. Cucumbers, tomatoes, radishes, lettuce, carrots, beets, broccoli, and marigolds are excellent companions. These plants either benefit from the nitrogen that peas fix in the soil or help with pest control, making your vegetable garden more productive and healthy.
Can I plant tomatoes near peas?
Yes, you can plant tomatoes near peas. Peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which tomatoes love, helping them grow strong and healthy. Just make sure to properly manage their water needs, as tomatoes prefer slightly drier soil than peas.
Why should I avoid planting peas near onions and garlic?
Avoid planting peas near onions and garlic because these allium family members release compounds that can inhibit the growth of peas.
Do cucumbers benefit from being planted with peas?
Yes, cucumbers love nitrogen, and peas are great at fixing nitrogen in the soil. This makes peas excellent companions for cucumbers, promoting healthier and more productive cucumber plants.
How do I manage pests in my pea plants?
Planting aromatic herbs and marigolds around peas can help manage pests. The strong scent of these plants repels common garden pests like aphids and Mexican bean beetles, allowing your peas to grow without chemical pesticides.
Can I grow peas in late summer?
Yes, you can grow peas in late summer. Peas thrive in cool weather, so planting them in late summer allows them to mature in the cooler temperatures of early fall, providing a good harvest season.
How much time do peas need to grow?
Peas typically need about 60 to 70 days to mature. The exact time can vary depending on the variety and growing conditions. Still, this timeframe generally allows them to develop fully and produce a good yield.
Are peas a type of legume?
Yes, peas are a type of legume. Legumes can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil, enriching the soil and benefitting other plants in the garden.
How can I ensure my peas grow well in the garden?
To ensure your peas grow well, plant them in early spring or late summer for cool weather, pair them with good garden mates like cucumbers and tomatoes, and avoid planting them near onions and garlic. Use aromatic herbs to repel pests and ensure they have enough sun and water. This will help your peas thrive and enhance the productivity of your vegetable garden.

Conclusion
Incorporating companion plants for peas in your garden is a smart strategy that maximizes space, enhances plant health, and boosts productivity. Each companion, whether it’s lettuce, nasturtium, or chive, brings unique benefits, creating a harmonious and thriving garden ecosystem. By understanding these plants’ specific needs and relationships, you can ensure they receive the time they need to grow and flourish.
Moreover, companion planting is not limited to peas alone. This practice can be applied to many other plants, providing a holistic approach to gardening. For example, the scent of marigolds repels pests. At the same time, the sprawling nature of cucumbers and pumpkins maximizes space, allowing them to grow without competing for resources.
By thoughtfully selecting companion plants, you create a garden that is productive in the cooler seasons and thrives in the summer. The benefits extend beyond the individual plants; they contribute to a balanced, pest-resistant, and nutrient-rich environment. This approach is essential for anyone interested in sustainable and efficient gardening. It is an invaluable technique for cultivating a vibrant and healthy garden.
So, whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting, integrating companion plants with your peas and other vegetables will undoubtedly lead to a more successful and enjoyable gardening experience. Embrace the natural synergies in your garden, and watch as your plants flourish together, each contributing to your green space’s overall health and productivity.

